Hip Replacement in Nagpur
Expert hip replacement surgery to help you move freely and live pain-free again.
What is Hip Replacement?
Hip replacement, or hip arthroplasty, is a surgery where a damaged hip joint is replaced with an artificial implant. It is usually advised for patients with severe arthritis, injury, or degeneration, causing constant pain.
The procedure restores smooth joint movement, reduces stiffness, and improves mobility. With advanced implants and techniques, patients regain confidence in daily activities. Overall, it helps relieve pain and greatly improves the quality of life.

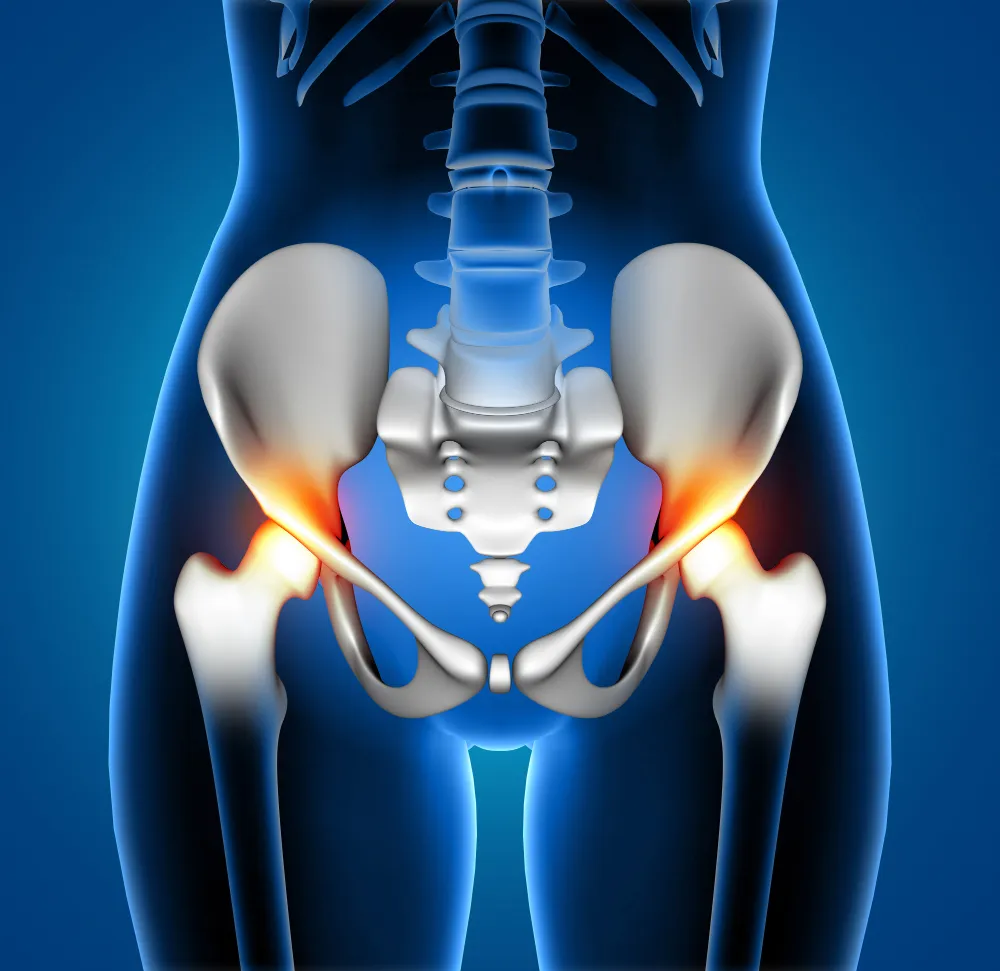
Anatomy of the Hip Joint
The hip is a ball-and-socket joint that enables smooth movement and supports body weight. A healthy hip is essential for walking, bending, and daily activities.
The hip is a ball-and-socket joint composed of:
- Femoral Head (Ball): The upper end of the femur (thigh bone).
- Acetabulum (Socket): A part of the pelvic bone that forms the socket.
- Cartilage: Smooth tissue covering the surfaces of the ball and socket, allowing for smooth movement.
- Ligaments and Muscles: Structures that stabilize and move the hip joint.
Indications for Hip Replacement
Hip replacement is advised when damage or degeneration causes constant pain and limited mobility. It is considered when other treatments no longer provide relief.
The common reasons for hip replacement include:
- Osteoarthritis: Degeneration of joint cartilage and underlying bone.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis: Chronic inflammatory disorder affecting the joints.
- Post-Traumatic Arthritis: Arthritis that develops after an injury.
- Avascular Necrosis: Death of bone tissue due to a lack of blood supply.
- Hip Fractures: Breaks in the hip bone.
- Hip Dysplasia: Abnormal development of the hip joint.
- Failed Previous Hip Surgery: Including hip resurfacing or prior replacement.
Types of Hip Replacement
Different hip replacement techniques are chosen based on the patient’s age, activity level, and extent of joint damage. Each type has unique benefits and indications. Below are the main types of hip replacement surgeries.
Total Hip Replacement (THR)
Both the femoral head and the acetabulum are replaced with prosthetic components.
Components:
- Metal or ceramic ball, metal stem, and a plastic or ceramic cup.
Partial Hip Replacement (Hemiarthroplasty)
Only the femoral head is replaced.
Indications:
- Typically used for certain types of hip fractures.
Hip Resurfacing
The femoral head is trimmed and capped with a smooth metal covering, and the acetabulum is fitted with a metal cup.
Indications:
- Generally, for younger, more active patients.
Surgical Procedure
Hip replacement surgery involves removing the damaged joint and replacing it with an artificial implant. The surgery is performed in well-defined steps to ensure precision and safety. Below given are the main stages of the surgical process, from anesthesia to closure.
Preoperative Preparation
- Evaluation: Medical history, physical examination, X-rays, and possibly MRI or CT scans.
- Preoperative Instructions: Discontinuing certain medications, fasting, and arranging postoperative care.
- Anesthesia: General anesthesia (patient is asleep) or regional anesthesia (spinal or epidural, numbing from the waist down).
Incision and Access
- Approaches: Posterior (back of the hip), lateral (side of the hip), or anterior (front of the hip). Each approach has different advantages and potential risks.
Removal of Damaged Tissue
- The surgeon removes the damaged femoral head and any diseased cartilage and bone from the acetabulum.
Implant Placement
- Acetabular Component: A metal cup is placed into the socket, and a plastic, metal, or ceramic liner is inserted into the cup.
- Femoral Component: A metal stem is inserted into the femur, and a metal or ceramic ball is attached to the stem.
Closure
- The surgeon closes the incision with stitches or staples and applies a dressing.
Postoperative Care
Proper care after hip replacement is essential to support healing, reduce pain, and lower the risk of complications. This phase ensures the patient transitions smoothly into recovery.
- Hospital Stay: Typically lasts 1 - 4 days, depending on the patient’s recovery progress.
- Pain Management: Medications including opioids, NSAIDs, and local anesthetics.
- Physical Therapy: Begins soon after surgery to restore movement and strength. Includes exercises to improve mobility, strengthen muscles, and ensure proper function of the new joint.
- Activity Restrictions: Avoiding certain movements that may dislocate the hip, such as bending too far or crossing legs.
- Follow-Up Visits: Regular check-ups with the surgeon to monitor recovery and implant function.
Risks and Complications
Like any major surgery, hip replacement carries certain risks that patients should be aware of. These are uncommon but important to consider before undergoing the procedure.
- Infection: Risk of surgical site infection.
- Blood Clots: Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) or pulmonary embolism (PE).
- Dislocation: The ball of the prosthesis can come out of the socket.
- Leg Length Discrepancy: One leg may end up shorter or longer than the other.
- Nerve Injury: Possible damage to surrounding nerves.
- Wear and Tear: Over time, the prosthetic components can wear out and may require revision surgery.
Advances in Hip Replacement
Modern innovations in hip replacement have made the surgery safer, less invasive, and more effective. These advancements provide patients with faster recovery and longer-lasting results.
- Minimally Invasive Techniques: Smaller incisions, less muscle damage, and faster recovery.
- Robotic-Assisted Surgery: Increased precision in implant placement.
- Custom 3D-Printed Implants: Tailored to fit the patient’s anatomy.
- Advanced Materials: Use of highly durable materials like cross-linked polyethylene, ceramics, and titanium.
Hip replacement is a well-established procedure that can significantly improve the lives of individuals suffering from severe hip joint damage. With advances in surgical techniques and implant materials, the outcomes of hip replacement surgeries continue to improve, offering patients greater pain relief and enhanced function.
Hip-Related Problems
The hip joint can be affected by several conditions that cause pain, stiffness, and restricted movement. Early diagnosis and treatment are important to prevent worsening damage. Some common problems are mentioned below:
Common Hip Problems:
- Osteoarthritis: Degenerative joint disease causing the breakdown of cartilage in the hip joint.
- Symptoms: Pain, stiffness, and decreased range of motion.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis: An autoimmune disorder leading to chronic inflammation of the hip joint.
- Symptoms: Pain, swelling, and joint damage.
- Hip Fractures: Breaks in the upper part of the femur (thigh bone) are often due to falls or osteoporosis.
- Symptoms: Severe pain, inability to move the hip, and leg shortening.
- Avascular Necrosis: Loss of blood supply to the femoral head, causing bone death.
- Symptoms: Pain and limited hip movement.
- Bursitis: Inflammation of the bursae (fluid-filled sacs that cushion the hip joint).
- Symptoms: Pain and tenderness, especially when moving the hip.
- Tendinitis: Inflammation of tendons around the hip joint.
- Symptoms: Pain and tenderness around the hip.
- Labral Tears: Tears in the ring of cartilage (labrum) that follows the outside rim of the hip joint socket.
- Symptoms: Pain, clicking, and instability.
Reasons Behind Hip Damage
Hip joint damage can occur due to aging, injuries, or certain medical conditions. Here are some common factors that contribute to hip problems:
- Age-Related Wear and Tear: Cartilage breakdown due to aging leads to osteoarthritis.
- Injuries: Trauma such as falls or accidents, causing fractures or dislocations.
- Genetic Predisposition: Inherited conditions or abnormalities affecting hip joint structure.
- Repetitive Stress: Overuse injuries from sports or heavy physical activity.
- Inflammatory Conditions: Diseases like rheumatoid arthritis causing joint inflammation and damage.
- Obesity: Excess weight putting additional stress on the hip joint.
Why Hip Replacement is Necessary
Hip replacement becomes essential when pain and mobility issues severely affect daily life. It is usually advised when conservative treatments fail to provide relief.
- Severe Pain: Persistent pain not relieved by medications or other treatments.
- Loss of Mobility and Function: Difficulty performing daily activities such as walking, sitting, or standing.
- Joint Deformity: Significant deformity affecting the alignment and mechanics of the hip.
- Failed Conservative Treatments: Ineffectiveness of non-surgical treatments like medications, physical therapy, and injections.
- Improvement in Quality of Life: Enhancing the ability to perform daily activities and overall well-being.
Latest Treatments for Hip Replacement
Modern advancements have made hip replacement safer, less invasive, and more effective. These treatments improve recovery, implant longevity, and patient outcomes.
Minimally Invasive Surgery
- Smaller incisions leading to reduced pain and quicker recovery.
Robotic-Assisted Surgery
- Enhanced precision in implant placement, improving outcomes and longevity of the hip replacement.
Custom 3D-Printed Implants
- Personalized implants designed to fit the patient’s anatomy perfectly.
Advanced Implant Materials
- Use of materials like highly cross-linked polyethylene, ceramics, and titanium for increased durability and reduced wear.
Enhanced Recovery Protocols
- Multimodal pain management, early mobilization, and patient education for faster recovery.
Benefits of Hip Replacement Surgery
Hip replacement surgery offers life-changing improvements for people struggling with severe hip problems. It not only relieves pain but also restores mobility and independence.
- Pain Relief: Significant reduction or elimination of hip pain.
- Improved Mobility and Function: Enhanced ability to walk, climb stairs, and perform daily activities.
- Correction of Joint Deformity: Restoring proper alignment and mechanics of the hip joint.
- Long-Term Durability: Many hip replacements last 15-20 years or more, providing lasting relief.
- Improved Quality of Life: Enhanced overall well-being, ability to participate in physical activities, and independence.
- High Success Rates: Hip replacement surgeries are generally very successful with high patient satisfaction.
In summary, hip-related problems can arise from various causes, including age-related wear and tear, injuries, and inflammatory conditions. Hip replacement becomes necessary when pain and disability significantly affect quality of life and conservative treatments fail. The latest treatments for hip replacement focus on minimally invasive techniques, robotic-assisted surgery, custom implants, and advanced materials, all aimed at improving outcomes and recovery times. The benefits of hip replacement surgery include significant pain relief, improved mobility, correction of joint deformities, and enhanced quality of life.
Get Back to an Active Life
Expert hip replacement can restore your mobility, strength, and independence.
Frequently Asked Questions
How long does it take to fully recover from hip replacement surgery?
Most people can resume light activities within 3-6 weeks. Full recovery, including strength and flexibility, usually takes 6-12 months with regular physiotherapy.
Can I return to sports or high-impact activities after hip replacement?
Low-impact activities like walking, swimming, and cycling are generally safe. High-impact sports should be discussed with your surgeon to avoid excess strain on the implant.
How long does a hip replacement implant typically last?
Modern implants often last 15-20 years or more. Longevity depends on activity level, weight, and implant material.
Will I need help at home after hip replacement surgery?
Yes, assistance is usually needed for the first few weeks for daily tasks. Preparing your home in advance can make recovery smoother.

