Knee Arthroscopy Surgeon in Nagpur
Restore Knee Health with Minimally Invasive Arthroscopic Surgery & Expert Care
What is Knee Arthroscopy
Knee arthroscopy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure used to diagnose and treat problems in the knee joint. During the procedure, an arthroscope (a small camera) is inserted into the knee joint through a small incision, allowing the surgeon to view the inside of the joint on a video monitor.
This technique enables the surgeon to diagnose and treat knee problems with less tissue damage than traditional open surgery. It is widely preferred because it causes less pain, smaller scars, and allows patients to return to daily activities much faster. The procedure is commonly used for both diagnosis and treatment of various knee conditions.
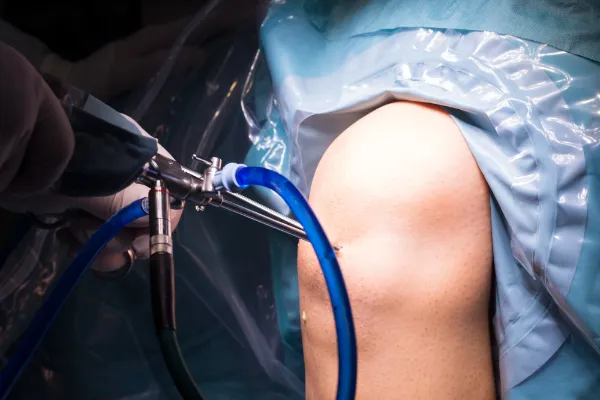
Complete Procedure
Preparation
- The patient is usually given regional or general anesthesia. The knee is cleaned and sterilized. A tourniquet might be applied to the thigh to reduce blood flow to the knee.
Incisions
- Small incisions (portals) are made around the knee joint. The arthroscope is inserted through one of the incisions.
Examination and Diagnosis
- The surgeon examines the inside of the knee joint using the camera. Saline solution is used to expand the joint and provide a clear view.
Treatment
- If necessary, surgical instruments are inserted through additional incisions. Common procedures include trimming damaged cartilage, repairing torn ligaments, or removing loose fragments.
Closure
- The instruments are removed, and the saline solution is drained. The incisions are closed with sutures or adhesive strips and covered with a bandage.
Recovery
- The patient is moved to a recovery room and monitored until the anesthesia wears off. Post-operative instructions are given, including care for the incisions, activity restrictions, and follow-up appointments.
Why Knee Arthroscopy is Necessary
Knee arthroscopy is often recommended when non-surgical treatments like medications, physiotherapy, or injections fail to relieve persistent knee pain or dysfunction. It allows the surgeon to both identify the exact cause of the problem and treat it effectively in the same sitting.
Knee arthroscopy is necessary to diagnose and treat various knee problems when non-surgical treatments have not provided relief. It is used for conditions such as:
- Torn meniscus (cartilage)
- Torn anterior or posterior cruciate ligaments (ACL/PCL)
- Inflamed or damaged synovium (lining of the joint)
- Misalignment of the patella (kneecap)
- Loose fragments of bone or cartilage
- Baker’s cyst (a fluid-filled swelling behind the knee)
- Knee sepsis (infection in the joint)
Knee arthroscopy not only helps relieve pain but also restores mobility and function to the joint. With timely treatment, patients can return to their daily activities with greater comfort and confidence.
Types of Knee Arthroscopy
Knee arthroscopy can serve both diagnostic and therapeutic purposes, depending on the patient’s condition. It allows the surgeon to first identify the underlying issue and, if needed, perform corrective procedures during the same session for faster relief.
Diagnostic Arthroscopy
- This type is done to carefully examine the inside of the knee joint and identify the exact cause of pain, stiffness, or swelling. It is particularly useful when imaging tests such as X-rays or MRIs are unclear or inconclusive.
Therapeutic Arthroscopy
- Once the problem is diagnosed, therapeutic arthroscopy allows the surgeon to repair, reconstruct, or remove damaged tissues through the same small incisions. This makes the treatment less invasive and helps in faster recovery compared to traditional surgery.
Common therapeutic arthroscopy procedures include:
- Meniscectomy: Removal of a torn or damaged meniscus.
- Meniscus Repair: Suturing and repairing the torn meniscus.
- Ligament Reconstruction: Reconstruction of injured ligaments such as the ACL or PCL.
- Chondroplasty: Smoothing and reshaping rough or damaged cartilage.
- Synovectomy: Removal of inflamed synovial tissue to relieve pain and swelling.
- Microfracture Surgery: Creating small holes in the bone to stimulate cartilage growth.
- Lateral Release: Releasing tight tissues on the outer side of the kneecap to improve alignment.
Benefits of Knee Arthroscopy
Knee arthroscopy is a modern, minimally invasive procedure that makes treatment safer and recovery faster compared to traditional surgery. It not only reduces discomfort but also helps patients regain mobility and confidence sooner.
Key Benefits
- Smaller incisions with minimal scarring
- Less post-operative pain and discomfort
- Quicker recovery and return to daily activities
- Lower risk of surgical complications
- Early mobility and faster rehabilitation
- High success rates with long-term relief
Risks & Complications of Knee Arthroscopy
While knee arthroscopy is generally safe and effective, like any surgical procedure, it carries some risks. These complications are uncommon and can usually be managed with timely medical care and proper follow-up.
Possible Risks
- Infection at the incision site or inside the joint
- Knee stiffness or temporary loss of flexibility
- Blood clots in the leg (rare)
- Swelling or fluid build-up in the joint
- Injury to nearby nerves or blood vessels (very rare)
Most patients recover smoothly, and these risks are minimized when the surgery is performed by an experienced orthopedic surgeon with proper post-operative care.
Recovery & Rehabilitation After Knee Arthroscopy
Recovery after knee arthroscopy is usually faster compared to open surgery, but it still requires proper care and rehabilitation. Following medical advice and physiotherapy plays a key role in ensuring smooth healing and regaining full mobility.
Typical Recovery Timeline
- First 1-2 days: Rest, ice application, and keeping the leg elevated to reduce swelling.
- 1-2 weeks: Light walking and daily activities with minimal discomfort.
- 3-4 weeks: Return to office work or non-strenuous routines.
- 4-6 weeks: Physiotherapy to improve strength and flexibility.
- 6-8 weeks: Most patients can resume normal activities.
- 3-6 months: Full recovery for sports or high-impact activities, if advised by the surgeon.
Take the First Step Toward Pain-Free Mobility
With advanced knee arthroscopy techniques, Dr. Manoj Pahukar provides accurate diagnosis, minimally invasive treatment, and faster recovery so you can get back on your feet with confidence.
Frequently Asked Questions
Will I need physiotherapy after knee arthroscopy?
Yes, physiotherapy plays a crucial role in regaining strength, flexibility, and mobility. Your doctor will recommend a tailored program for your recovery.
Is knee arthroscopy painful?
Since the procedure is minimally invasive, most patients experience only mild discomfort post-surgery, which is manageable with prescribed medications.
When can I return to work or daily activities?
Light activities can be resumed within 1-2 weeks, while more physically demanding tasks may require 4-6 weeks or longer, depending on your healing progress.
Are there risks involved with knee arthroscopy?
Will I need to stay in the hospital after knee arthroscopy?
Most knee arthroscopies are performed as day-care procedures, meaning you can go home the same day after recovery from anesthesia.
Can knee arthroscopy prevent the need for knee replacement?
In many cases, yes. By addressing issues like torn cartilage or ligament injuries early, knee arthroscopy can help preserve joint health and delay or even prevent the need for knee replacement surgery.
Is knee arthroscopy done under general anesthesia?
It can be performed under general, spinal, or regional anesthesia. The choice depends on the patient’s health condition and the surgeon’s recommendation.
Will I need crutches or a knee brace after the surgery?
Most patients use crutches for a few days to a week. A knee brace may be prescribed depending on the type of repair performed.
Are there long-term restrictions after knee arthroscopy?
High-impact activities like jumping or running should be avoided for a few weeks or months. Low-impact exercises such as swimming, cycling, and walking are usually encouraged.

